Code
tanks <- function (n_tanks = 47, n_obs = 5, n_reps = 100, fixedest = 50)
{
temp <- as.matrix(rep(n_tanks, n_reps))
temp <- apply(temp, 1, sample, size = n_obs)
temp <- t(apply(temp, 2, tanks.ests, fixedest))
temp
}The function tanks simulates n_reps battles with n_obs serial numbers recorded for each battle. The argument n_tanks is the number of tanks that the Germans had. The argument fixedest is the expert’s best guess.
tanks <- function (n_tanks = 47, n_obs = 5, n_reps = 100, fixedest = 50)
{
temp <- as.matrix(rep(n_tanks, n_reps))
temp <- apply(temp, 1, sample, size = n_obs)
temp <- t(apply(temp, 2, tanks.ests, fixedest))
temp
}The function tank.ests runs on a sample of observed serial numbers. Each of the vector values is the result of a student supplied estimator. These need to be changed to reflect the class’ ideas.
tanks.ests <- function (x = stop("Argument 'x' is missing"), fixedest = 125)
{
n <- length(x)
nodd <- n %% 2 == 1
ests <- rep(NA, 16)
xbar <- mean(x)
xmedian <- median(x)
xn <- max(x)
xvar <- var(x)
xstddev <- sqrt(xvar)
x1 <- min(x)
rng <- c(-1,1)%*%range(x)
xsum <- sum(x)
xnm1 <- sort(x)[n-1]
ests[1] <- 2 * xbar
ests[2] <- 2 * xmedian
ests[3] <- xn
ests[4] <- xbar + 2*xstddev
ests[5] <- xbar + 3*xstddev
ests[6] <- nodd * (xmedian + x[(n+1)/2 + 1]) + !nodd * (xmedian + x[n/2 + 1])
ests[7] <- xn + xmedian
#
y = sort(x)
z = c(NA,y[-n])
ests[8] <- xn + mean(y-z, na.rm = TRUE)
z = c(0,y[-n])
ests[9] <- xn + mean(y-z)
z = c(1,y[-n])
ests[10] <- xn + mean(y-z)
ests[11] <- (3*xn - x1)/2
ests[12] <- (5*xn - xbar)/3
ests[13] <- 3*xmedian + rng
ests[14] <- xn
ests[15] <- xn * ((n+1)/n) - 1
ests[16] <- fixedest
names(ests) <- c("2*xbar", "2*m", "x[n]", "xbar+2s", "xbar+3s", "m + next largest",
"x[n] + m", "x[n]+mean(x -lag(x))", "x[n]+mean(x -lag(x) w/ 0)",
"x[n]+mean(x -lag(x) w/ 1)", "(3x[n]-x[1])/2", "(5*x[n]-xbar)/3",
"3m + range(x)", "x[n]", "UMVUE", fixedest)
ests
#ests[1] <- xn
#ests[2] <- 2 * xbar
#ests[3] <- xn + x1
#ests[4] <- xn + rng/2
#ests[5] <- xbar + xstddev
#ests[6] <- 2 * xmedian
#ests[7] <- xn + xnm1
#ests[8] <- 2*xn - x1
#ests[9] <- xsum
#ests[10] <- xn * ((n+1)/n) - 1
#ests[11] <- fixedest
#names(ests) <- c("x[n]","2*xbar", "x[n]+x[1]", "x[n]+R/2", "xbar+s", "2*m",
# "x[n]+x[n-1]","2x[n]-x[1]","sum(x)", "UMVUE",fixedest)
#ests
}The function tanks.descriptives computes descriptive statistics for each of the estimators in tanks.ests.
tanks.descriptives <- function (n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 100, fixedest = 50)
{
temp <- tanks(n, obs, reps, fixedest)
means <- apply(temp, 2, mean)
stddevs <- sqrt(apply(temp, 2, var))
medians <- apply(temp, 2, median)
bias <- means - n
mse <- bias^2 + stddevs^2
t(cbind(means, stddevs, medians, bias, mse))
}The individual estimates computed for the samples from each battle can be plotted. This allows us to compare location and dispersion statistics — center and spread. tanks.plots2 is intended to be an “improved” version of tanks.plots. Both plots use traditional lattice boxplots and there is a ggplot plot as well.
### Load the lattice package
p_load(lattice)
tanks.plots <- function (n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 100, fixedest = 50)
{
temp <- tanks(n, obs, reps, fixedest)
tanknames <- attributes(temp)$dimnames[[2]]
dims <- dim(temp)
temp <- as.vector(t(temp))
temp <- cbind(temp, rep(1:dims[2], dims[1]))
bwplot(factor(temp[, 2], labels = tanknames) ~
temp[, 1], xlab = "Number of Tanks",
ylab = "Estimator")
}
tanks.plots2 <- function (n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 100, fixedest = 50)
{
temp <- tanks(n, obs, reps, fixedest)
tanknames <- attributes(temp)$dimnames[[2]]
dims <- dim(temp)
temp <- as.vector(t(temp))
temp <- cbind(temp, rep(1:dims[2], dims[1]))
bwplot(factor(temp[, 2], labels = tanknames) ~
temp[, 1], xlab = "Number of Tanks",
ylab = "Estimator", panel = function (x ,
y , vref = n, ... )
{
panel.bwplot(x, y)
panel.abline(v = vref, lty = 2)
}, vref = n)
}
p_load(ggplot2)
p_load(tidyverse)
tanks.plots3 <- function (n = 84, obs = 5, reps = 100, fixedest = 87)
{
temp <- tanks(n, obs, reps, fixedest)
tanknames <- attributes(temp)$dimnames[[2]]
dims <- dim(temp)
temp <- as.vector(t(temp))
temp <- cbind(temp, rep(1:dims[2], dims[1]))
temp <- as_tibble(temp)
names(temp) <- c("Estimate", "Estimator")
temp$Estimator <- factor(temp$Estimator)
ggplot(temp, aes(x=Estimator, y=Estimate)) +
geom_boxplot(alpha=0.7) +
stat_summary(fun=mean, geom="point", shape=20, size=5, color="red", fill="red") +
theme(legend.position="none") +
scale_fill_brewer(palette="Set1") +
geom_hline(yintercept = n, alpha = 0.5, color = "blue", lty = 1) +
coord_flip()
}
tanks.plots4 <- function (n = 84, obs = 5, reps = 100, fixedest = 87)
{
temp <- tanks(n, obs, reps, fixedest)
temp <- melt(temp)
names(temp) <- c("RowID","Estimator","Estimate")
ggplot(temp, aes(x=reorder(Estimator, Estimate, FUN=mean), y=Estimate)) +
geom_boxplot(alpha=0.7) +
stat_summary(fun=mean, geom="point", shape=20, size=5, color="red", fill="red") +
theme(legend.position="none") +
xlab("Estimator") +
scale_fill_brewer(palette="Set1") +
geom_hline(yintercept = n, alpha = 0.5, color = "blue", lty = 1) +
coord_flip()
}
tanks.plots5 <- function (n = 84, obs = 5, reps = 100, fixedest = 87)
{
temp <- tanks(n, obs, reps, fixedest)
temp <- melt(temp)
names(temp) <- c("RowID","Estimator","Estimate")
ggplot(temp, aes(x=reorder(Estimator, Estimate, FUN=mean), y=Estimate)) +
geom_violin(alpha=0.7) +
stat_summary(fun=mean, geom="point", shape=20, size=5, color="red", fill="red") +
theme(legend.position="none") +
xlab("Estimator") +
scale_fill_brewer(palette="Set1") +
geom_hline(yintercept = n, alpha = 0.5, color = "blue", lty = 1) +
coord_flip()
}The class’ estimators can be compared using the functions defined above.
### Compute descriptive stats
t(tanks.descriptives(n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 10000, fixedest = 50)) means stddevs medians bias mse
2*xbar 48.14516 11.571031 48.00000 1.145160 135.20014
2*m 48.10140 17.023910 48.00000 1.101400 291.02658
x[n] 40.09400 6.225531 42.00000 -6.906000 86.45008
xbar+2s 50.67561 8.970541 51.65893 3.675611 93.98072
xbar+3s 63.97713 11.866761 65.09947 16.977127 429.04285
m + next largest 48.15770 18.681251 48.00000 1.157700 350.32940
x[n] + m 64.14470 12.548231 65.00000 17.144700 451.39885
x[n]+mean(x -lag(x)) 48.10440 7.624107 50.00000 1.104400 59.34671
x[n]+mean(x -lag(x) w/ 0) 48.11280 7.470638 50.40000 1.112800 57.04875
x[n]+mean(x -lag(x) w/ 1) 47.91280 7.470638 50.20000 0.912800 56.64363
(3x[n]-x[1])/2 56.11480 9.244018 58.00000 9.114800 168.53145
(5*x[n]-xbar)/3 58.79914 9.245939 61.13333 11.799140 224.70709
3m + range(x) 104.19370 26.563252 105.00000 57.193700 3976.72566
x[n] 40.09400 6.225531 42.00000 -6.906000 86.45008
UMVUE 47.11280 7.470638 49.40000 0.112800 55.82315
50 50.00000 0.000000 50.00000 3.000000 9.00000 ### Plot the estimates from each of the estimators
tanks.plots(n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 10000, fixedest = 50)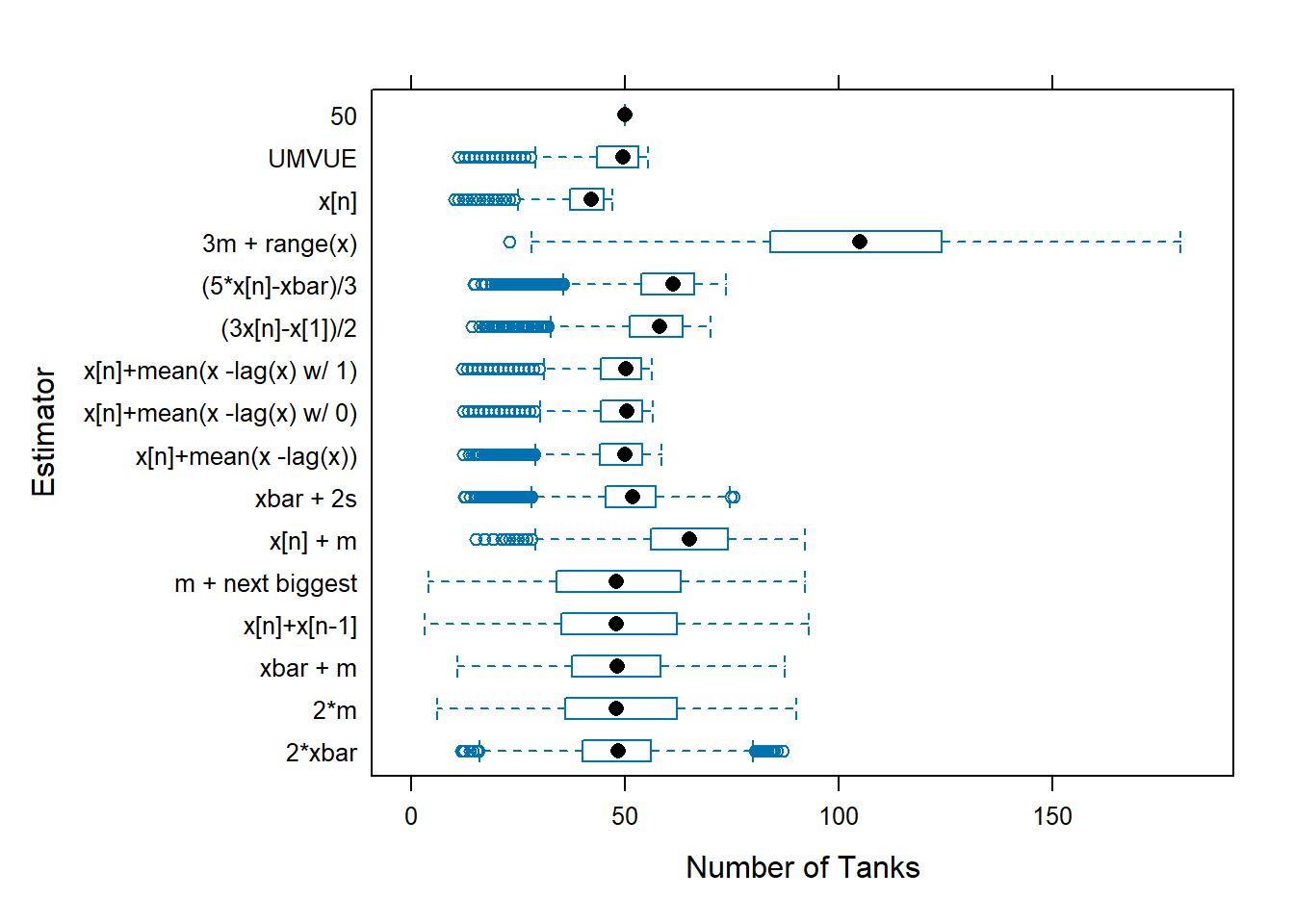
### Plot the estimates from each of the estimators
tanks.plots2(n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 10000, fixedest = 50)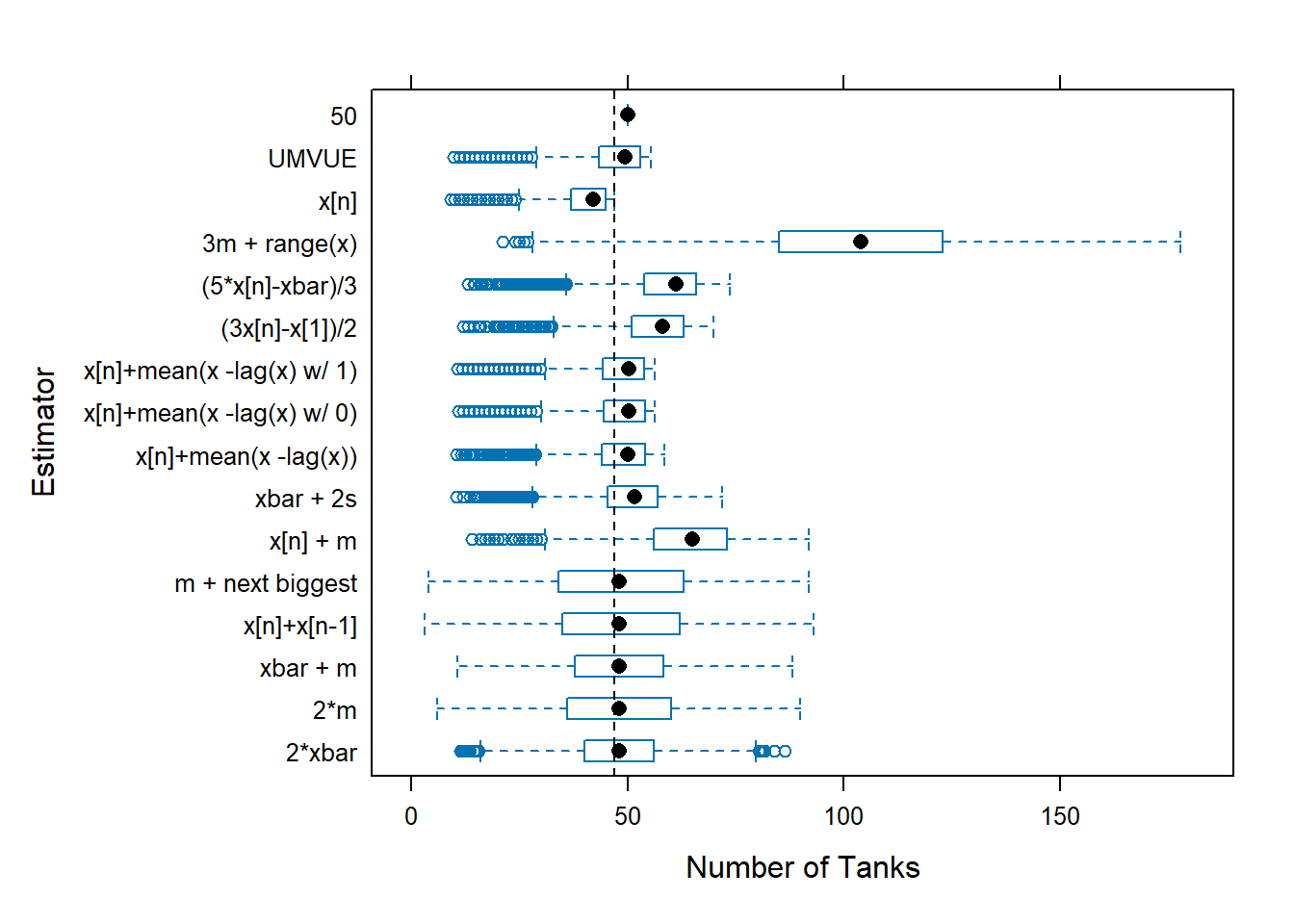
### Plot the estimates from each of the estimators
tanks.plots4(n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 10000, fixedest = 50)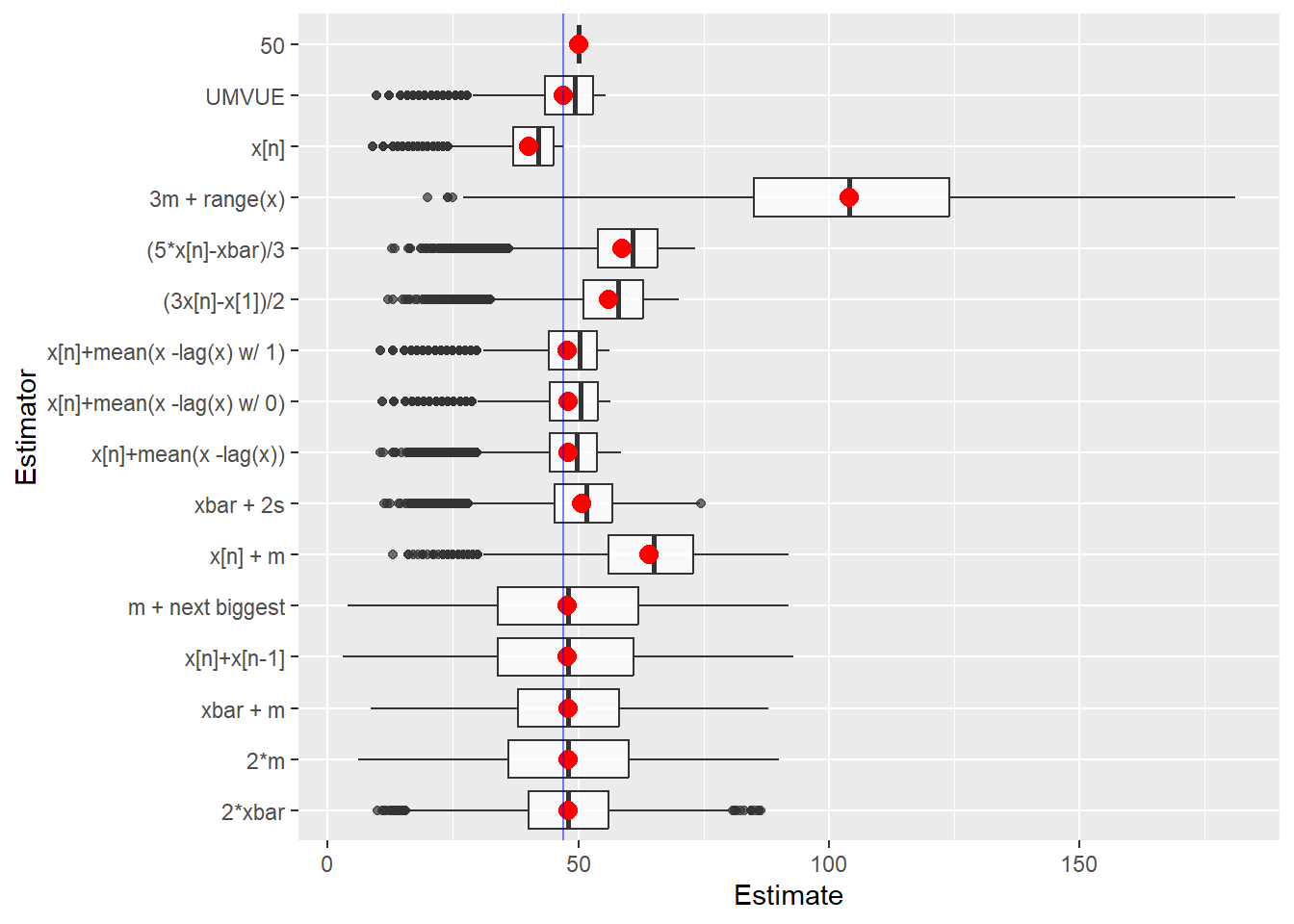
### Plot the estimates from each of the estimators
tanks.plots5(n = 47, obs = 5, reps = 10000, fixedest = 50)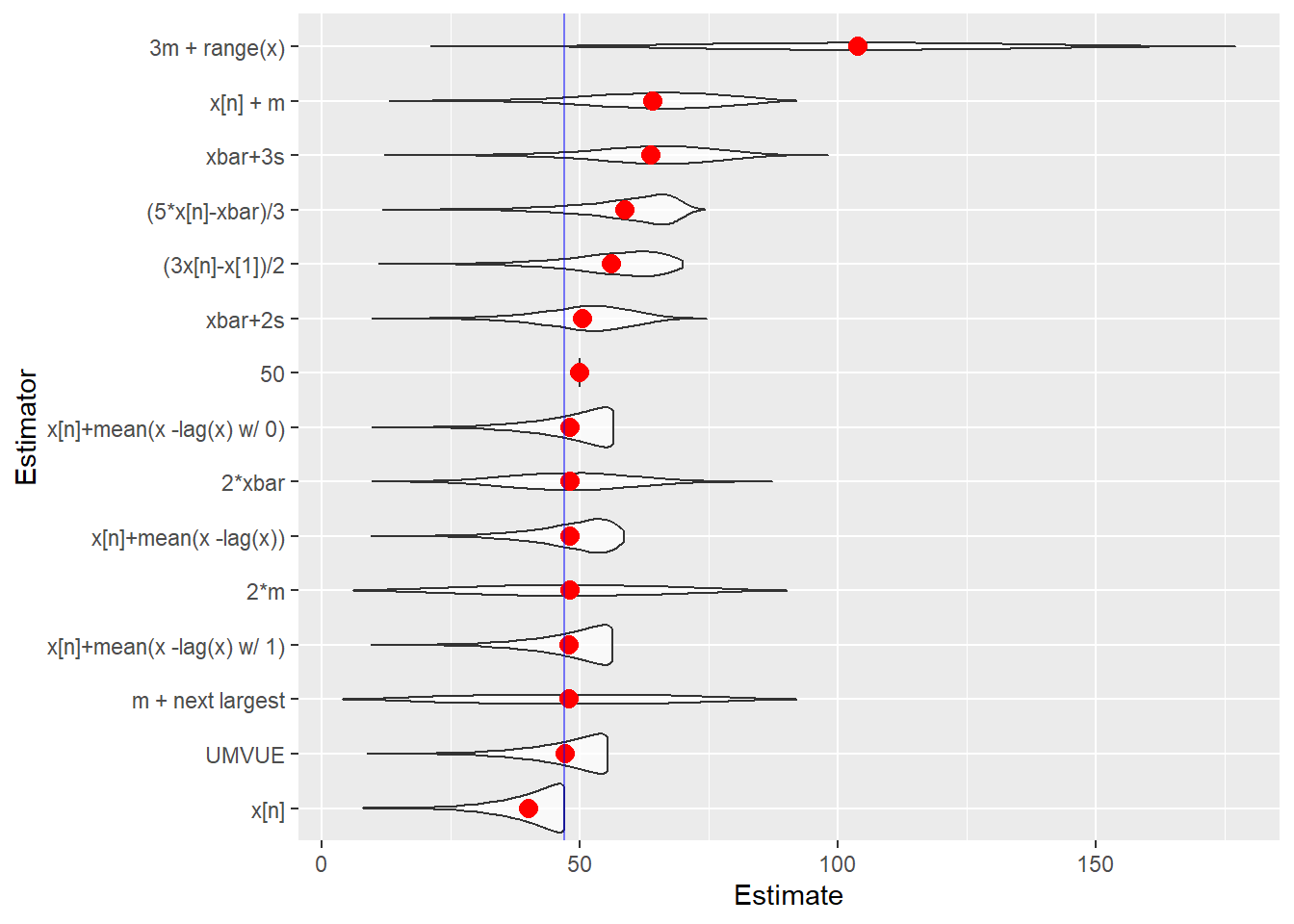
Note that \widehat{N} = X_{(n)} \frac{n+1}{n} - 1 is UMVUE for N when the X_i are i.i.d. DU(1,N).